The main characteristic of diabetes is an excess of sugar (glucose) in the blood. We even get sugar from food. Eg bread, rice, pasta, dairy products, etc. The body uses this sugar as energy needed to run, play, swim, etc. Glucose is converted into energy in the cell. In order for the blood sugar to pass into the cell, you need a key that will open the cell door. This is the key to insulin. When insulin is not present or is insufficient, glucose can no longer enter the cell, remains in the blood, and its amount in the blood is high.
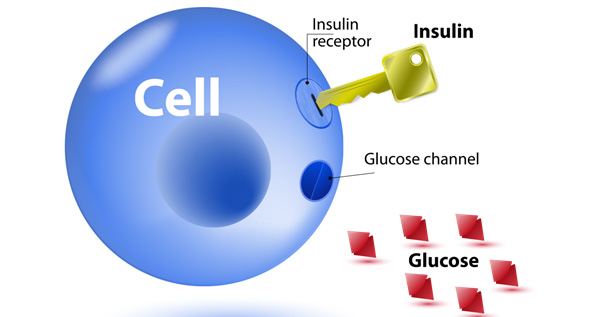
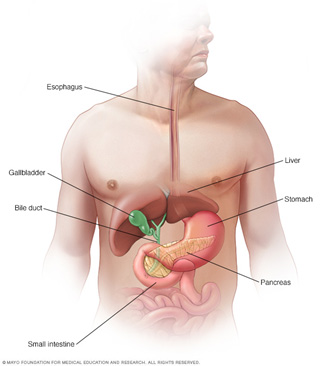
Insulin is produced in the beta cells of the pancreas. The pancreas is the digestive organ, also called the pancreas. Other substances (enzymes) are also produced in the pancreas, which then enter the intestines and provide digestion. It should be noted that digestive function is not impaired during diabetes.
As for diabetes, the most common are the first and second types of diabetes.
Type 1 diabetes is usually found in children. It is at this time that the beta cells that produce insulin are damaged. The body itself produces antibodies against these cells and slowly destroys its own cells. By the time diabetes is already detected, 90% of the cells have already been destroyed.
With such diabetes, it is necessary to inject insulin externally, so millions of people around the world need insulin injections.
It is unfortunately impossible to insure yourself against type 1 diabetes. Doctors do not know in advance who will be affected and who will not. This type of diabetes is also called insulin-dependent, also known as juvenile diabetes.
Another form of diabetes, type 2, develops mainly in adults. Treatment at this time is with tablets, although in some cases insulin is also needed.
It should be noted that in recent years, the incidence of type 2 in children and adolescents, especially against the background of obesity, has increased worldwide.
It is also known as a different type of diabetes MODY, which progresses more easily, often does not require insulin and is mostly found as a familial form.
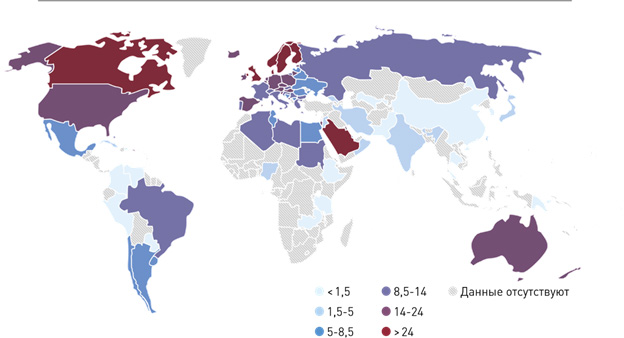
The figure below shows the number of new cases of type I diabetes aged 0-14 per 100,000 children per year.
Glucose, as already mentioned, is found in the blood as a result of the processing of food. Part is converted into energy, and part is stored in the liver, muscles, adipose tissue as a supply, which is then broken down into glucose when needed (interval between meals, during exercise, etc.). It all boils down to anti-insulin hormones - glucagon, adrenaline and more. Sh. Through.
Through these regulatory factors, glucose levels range from 3.3 to 5.5 mmol / L and 7.8 mmol / L 2 h after a meal. Such numbers are called normoglycemia. Elevated blood sugar is called hyperglycemia, while reduced blood sugar is called hypoglycemia.






