In order to perfectly manage diabetes, have sugar in the norm and avoid complications, we need self-control and constant monitoring.
It should be remembered that the main essence of self-control is not only regular monitoring of glucose levels, but also the need to analyze the results obtained, independent dose adjustment and plan certain actions to correct the condition.
Glucose monitoring can be compared to controlling the fuel level in a car. Care should be taken not to lower or raise the sugar level above the norm.
The purpose of monitoring is to keep the sugar levels as close as possible to the norm. Such a condition is called diabetes compensation, and a condition in which blood glucose is constantly or frequently elevated is called diabetic decompensation.
Often small children are afraid of snoring, resisting us during the analysis. They should explain that the tingling is not painful. To prove this we can also take an analysis and show that nothing is dangerous.
In type 1 diabetes, it is important to check your glucose levels daily, usually before meals and at bedtime. We define glycemia, To evaluate how the already done insulin do zam was affected and decide how many units to do this time. We also need to measure it periodically during the night so that we do not have night hypoglycemia. Especially if morning hyperglycemia is frequent, at this time the child wakes up tired, with a headache, often has bad dreams.
We will need more frequent measurements during viral and infectious diseases, physical activity, changes in the usual daily routine, etc.
Blood glucose self-control
We monitor glucose at home using glucometers. Glucometers differ from each other in shape, size, required blood volume, memory capacity, and so on.

Different types of glucometers
There are two types of glucometers: photometric and sensory.
The principle of operation of photometric cameras is based on the optical perception of color, as well as the human eye. It measures the color of the test area produced by exposure to blood glucose with a special substance coated on the test sticks (the higher the blood glucose, the darker the color).
The principle of the sensory glucometer is based on the electrochemical reaction, during which an electric current is determined, which is also generated by the action of glucose on the blood with a chemical substance applied to the test sticks.
Glucose is measured in mmol / L or mg / dL. To convert mmol / l to mg / dL, multiply by 18 and vice versa. For example: 10 mmol / l is equivalent to 180 mg / dL. Both indicators are used in Georgia.
It should be noted that due to a number of advantages, sensor glucometers have gained wider use in recent years (high accuracy, lower blood pressure, etc.).
Sensory glucometer
Some glucometers measure blood sugar, while others measure blood plasma. It is usually 10-12% more important when measured in plasma than when measured in blood.
As for the measurement accuracy, with two glucometers at the same time, the difference is allowed to be 10-15%. To avoid errors, it is desirable to control with the same device.
An erroneous figure can give us:
Sugar on the fingers;
When the finger is wet;
The sticks are expired;
Blood is not enough;
There is an alcohol residue on the finger;
Hold your finger firmly to get a drop of blood.
The incision is made through a special incision - a lancet, which is practically painless. The sting is preferably on the lateral surface of the finger, as it is less painful and is easily digested.

Blood Lancet
Glucometer accu-chek performa
There is a non-contact type of glucometer when a sensor is attached to the skin (mainly on the upper extremity) that automatically measures and stores glucose readings throughout the day and night. The data can be read by scanning, which takes just one second and the clothes do not interfere. For each scan we get the data for the last 8 hours and an arrow pointing in the direction of the glucose change.
The sensor is waterproof, does not damage during showering, swimming, exercise.
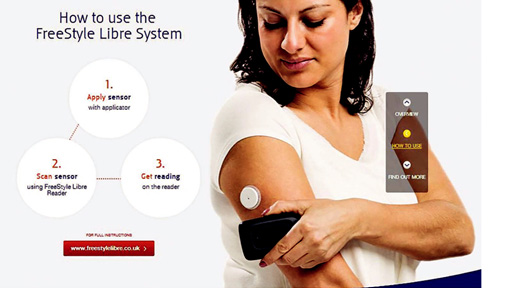
Contactless glucometer sensor
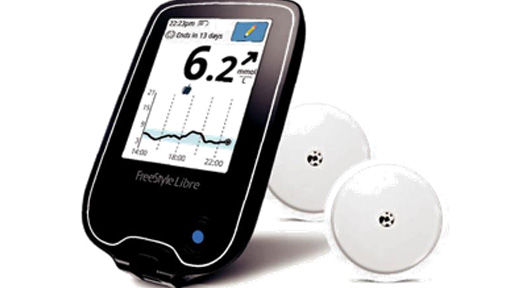
Contactless glucometer
It is important for everyone to keep a self-monitoring diary, where we will record daily measured glucose levels and insulin doses. The possible causes of hypo- or hyperglycemia, physical exertion, etc. can be listed in the note box. A record diary should be discussed with a physician who can assess the degree of compensation, give us some tips and recommendations.
There is also a device for glucose control called the Continuous Glucose Monitoring System. It detects glucose every 5 minutes for several days via a subcutaneous sensor. But because the system determines glucose not in the blood but in the intracellular fluid, it can rarely be used to assess glycemia at a particular point in time. However, sensor readings help us to assess the tendency for glucose changes, e.g., during the development of sudden hypoglycemia at night.
Urine sugar and acetone monitoring
When blood sugar reaches a certain level, for example, 9-10 mmol / l, the kidneys can no longer retain glucose and the sugar passes into the urine. This indicator of glycemia is called the renal threshold.
Frequent urination caused by high glycemia causes dehydration and dehydration of the body, as a result of which the patient develops an increased feeling of thirst and therefore he needs to consume large amounts of fluid.
Urine glucose and acetone are measured using special test sticks. Glucose measurements indicate the importance of glucose in the last few hours and do not give us an idea of the current rate. Therefore it has less diagnostic value.
More important is the content of acetone (ketones) in the urine.
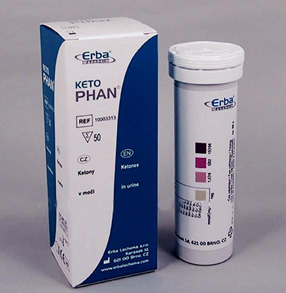
Tests for the detection of keto cells (acetone) in urine

Determination of glucose and acetone in urine
In case of insulin deficiency, as we have already said, we can no longer use glucose as an energy source. In this case, fats are used to get energy, which does not need insulin to get to the cell. As a result, the body begins to burn fat and consequently lose weight.
As for the fat that gets into the cell, it breaks down into fatty acids and releases energy. Ketones are formed in the liver from fatty acids. Ketones are also excreted in the urine.
Ketones are dangerous for the body. A large number of them cause nausea and vomiting, abdominal pain, shortness of breath and in some cases even ketoacidosis (hyperglycemic) coma.
Ketones can appear even when we are hungry for a long time, we do not take carbohydrates at all. Insulin may be enough at this time, but we do not have glucose and therefore we start to get the energy we need to survive by breaking down fats again.
Thus, when there is neither glucose nor acetone in the urine, the rate is normal:
If, there is no glucose and we have ketones - ie. Carbohydrate deficiency;
If you have both glucose and acetone, you have insulin deficiency and need to increase the dose of short / ultra-short insulin based on your doctor's advice;
Frequent determination of acetone makes no sense. However it is necessary in a number of cases.
In particular:
If your blood sugar level exceeds 15 mmol / L (270 mg / dL) within 24 hours;
If, glucosuria has a persistent character, during various diseases, acute infections;
During nausea and vomiting;
Before intense physical activity;
Scheme of glycated hemoglobin production
As far back as the 70s of the 20th century, the ability of glucose to form a compound with proteins (albumin, collagen, hemoglobin, etc.) was observed. This process is called glycation. When diabetes is decompensated, protein glycosylation is increased. Glucose involved in proteins causes protein dysfunction.
ცილები შედიან ნერვულ, სისხლძარღვოვან, თირკმლის და ორგანიზმის სხვა ქსოვილთა შემადგენლობაში.
ცილების ფუნქციის დარღვევა კი გართულებების განვითარებას უწყობს ხელს.
Thus, erythrocytes also accumulate glucose as a compound with hemoglobin. The lifespan of erythrocytes is about three months. Thus the degree of glycation of hemoglobin depends on the glucose levels of the last three months. The hemoglobin associated with such glucose is called glycated hemoglobin. The higher the blood sugar concentration, the higher the value of glycated hemoglobin
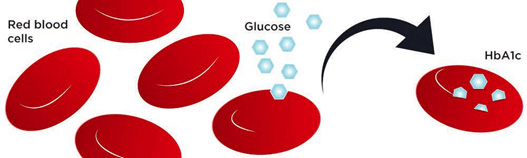
Scheme of glycated hemoglobin production
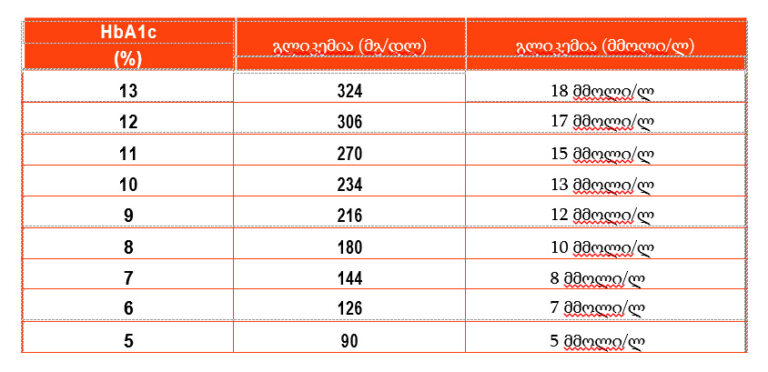
They mainly define the HbA1c fraction of glycated hemoglobin. The analysis is performed in the laboratory and according to its importance we can judge the degree of compensation of carbohydrate metabolism and the average levels of glucose in the blood in the last 2-3 months.
There is a fairly accurate correlation between glycated hemoglobin output and mean day-to-day sugar levels.
Blood glycated hemoglobin index
Correspondence with glucose levels