The practical use of insulin was a real revolution in the treatment of diabetes. Today diabetes is no longer a deadly disease and we have the opportunity to save many lives.
Unfortunately a complete cure for diabetes is nowadays impossible. In all countries of the world, insulin injections remain the sole and primary means of treating type 1 diabetes.
In 1869, Paul Langerhans, a Berlin student, discovered cell clumps during microscopic examination of the pancreas. Their role in the regulation of carbohydrate metabolism was later established. Today these cells are called Langerhans Islands.
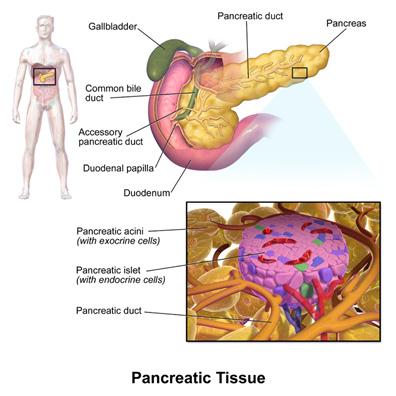
Then there were numerous attempts to secrete a glucose-lowering substance from the pancreas, and finally
1921 In Canada, st. In Toronto, Frederick Bunting and Charles Best extracted a substance from the calf's pancreas that lowered blood glucose levels in diabetic dogs. This substance is called insulin (Latin word insula - means island), it was the greatest event in the history of medicine, for which in 1923 he was awarded the Nobel Prize.

Charles Best and Frederick Bunting
And Bunting's birthday - November 14, is celebrated annually as International Diabetes Day.
The first insulin in the world was given to 14-year-old Leonard Thompson on January 11, 1922. Soon mass production of insulin began, initially with insulin coming in the form of a powder that was dissolved in a solvent immediately before injection.
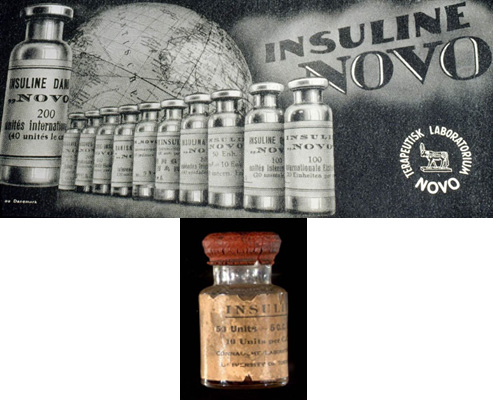
The first commercial insulin

Leonard Thompson years later
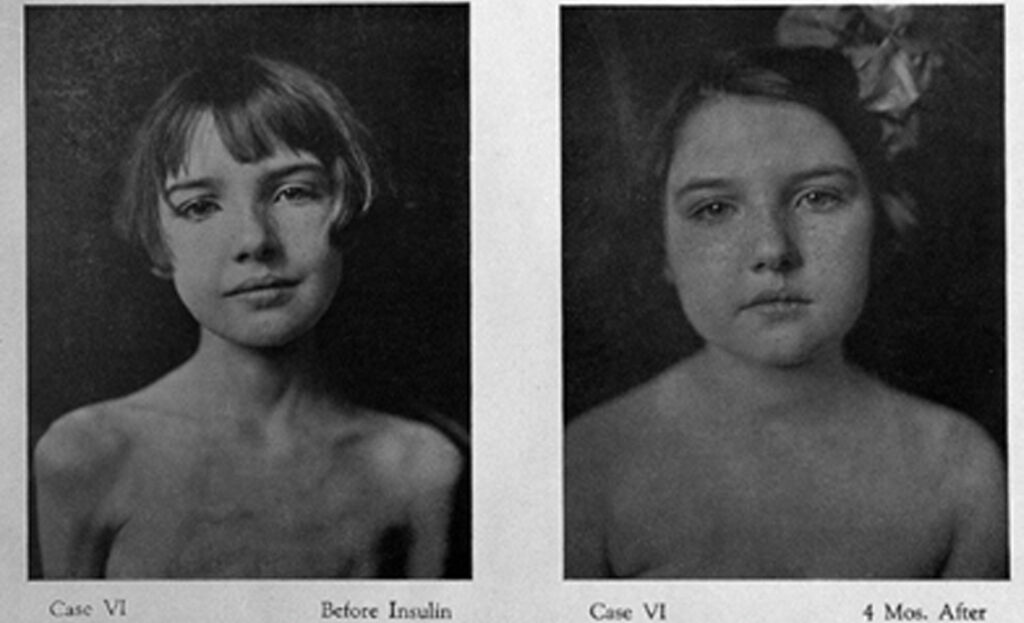

One of the first patients to receive insulin therapy and
After insulin therapy
Insulin is a substance with a protein structure. Its structure was first deciphered by Frederick Sanger in 1951. It turned out that insulin consists of two chains - A and B, which are connected to each other by sulfide bridges.
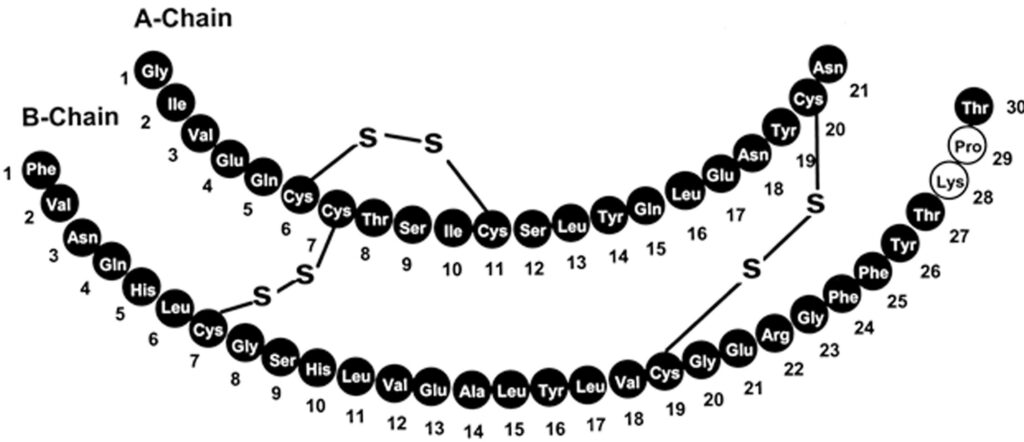
The structure of insulin
By studying the structure of insulin, it became possible to produce synthetic insulins. Frederick Sanger received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1958 for this merit.
In the past, animal insulins (pork, bull) were used, which were accompanied by various complications. Even the highest quality human insulins and insulin analogues obtained through genetic engineering are currently used.
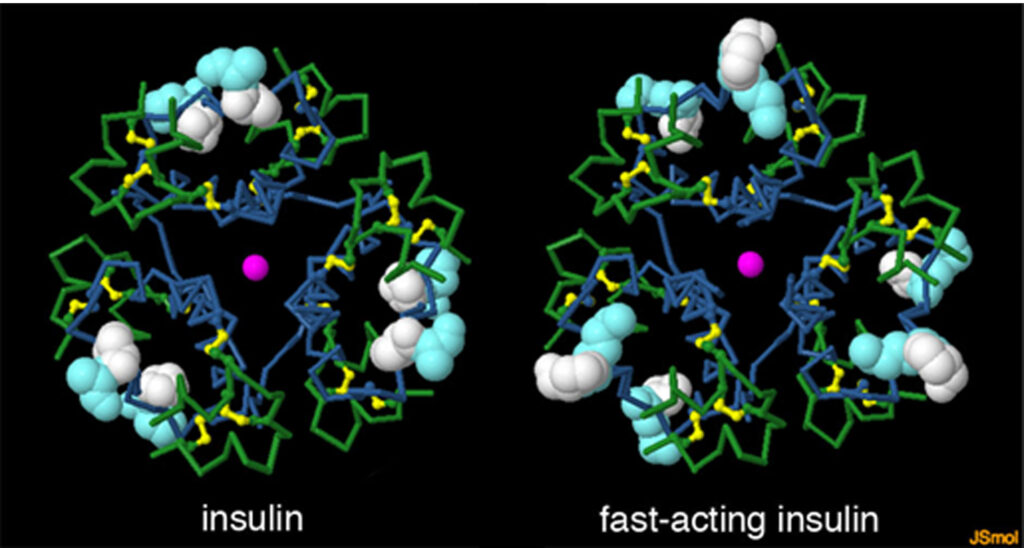
Spatial structure of insulin
You can find ads in popular publications or on the Internet where they promise to cure diabetes, be it physiotherapy procedures, laser therapy or massage of the pancreas. As well as various plant kits, electromagnetic and other fields, biowell treatment with psychics, etc.
Of course, all these measures are in vain, and reducing or completely eliminating insulin doses can lead to a life-threatening condition - ketoacidosis coma.
The dose of insulin and the treatment regimen are determined by the doctor, and we should be able to do the selected dose correctly and know the rules of how to change the insulin doses depending on the level of glucose in the blood.
Insulin therapy
As we already know, in healthy people, the pancreas releases insulin into the bloodstream as soon as it is ingested. The more carbohydrates we get, the more insulin is released. Such insulin Bolus insulin Is called. At the same time, between meals, during sleep at night, the pancreas also secretes a small amount of insulin, which is needed for the body to function. Even this insulin Basal Insulin is called.
During treatment, to get the best results, we must imitate the physiological secretion of insulin. For this we need basal and bolus insulins.
Short-acting, ultra-short, prolonged and long-acting insulins are selected according to the duration of action.
Bolus insulins include short-acting and ultra-short-acting insulins, and basal insulin long-acting and long-acting insulins.
Short Action insulin is human insulin.
Short-acting insulins are: Actrapid (Novo Nordisk), Humulin R (Lilly)
Short-acting insulin
It is a colorless transparent liquid. It takes effect 20-30 minutes after injection, reaches its peak in 2-4 hours and ends in 6 hours. Thus food should be taken within half an hour of doing so so that the periods of glucose absorption and insulin action coincide. We take food according to the current dose.
Too little will cause hypoglycemia, and too much will cause hyperglycemia. Too little will cause hypoglycemia and too much will cause hyperglycemia.
Two hours after the injection, when the short-acting insulin is at its peak, an additional meal is necessary, so called. It hurts because insulin works at this time, and the sugar in the food is no longer in the blood.
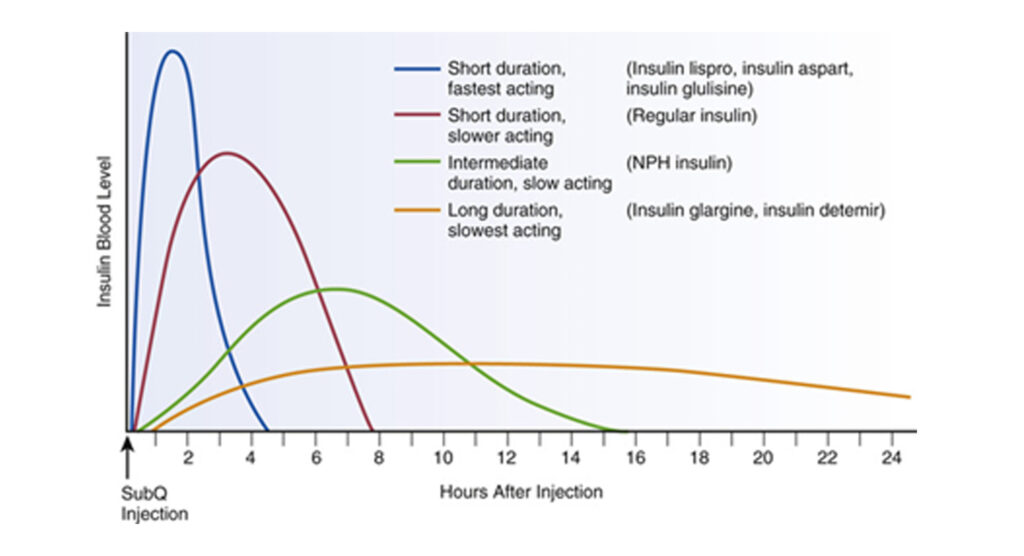
Profile of action of different types of insulin
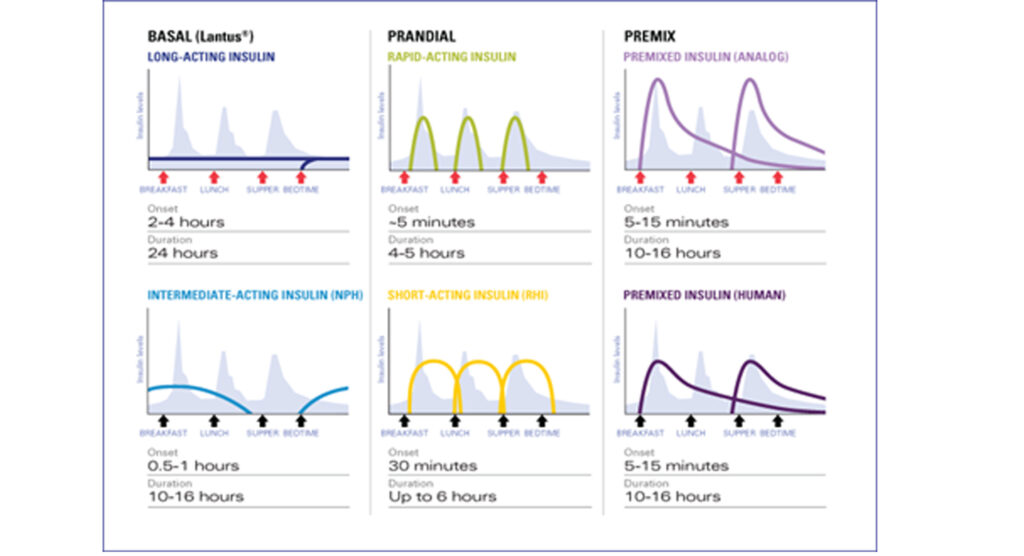
Profile of action of different types of insulin
Ultra-short Action insulins are insulin analogues. Is a transparent, colorless liquid.
Ultra-short-acting insulins are: Novorapid – Aspart ((Novo Nordisk), Humalog – Lispro (Lilly), Apidra – Glulisine (Sanofi Aventis)

Ultra-short-acting insulin
It takes effect as soon as it is inserted (in 5-15 minutes). Because of this the interval protection is not necessary at all. In some cases it is even possible to enter it after feeding. It is especially useful in small children when it is difficult to determine in advance how much food they will receive.
Ultra-short-acting insulins peak in 1-2 hours, which exactly coincides with the food processing period. Does not require additional feeding, feeding. Duration of action is 4-5 hours. There is less risk of hypoglycemia. Because of all this, it is especially convenient, especially in the age of transition.
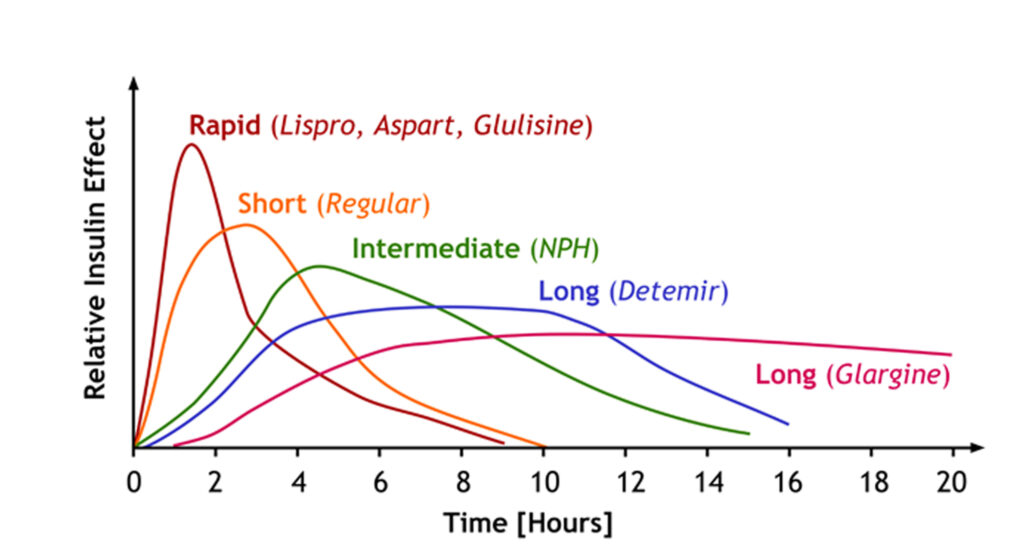
Profile of action of different types of insulin
Extended Action Insulins - Insulatard (Novo Nordisk), Humulin N (Lilly)

Prolonged-acting insulin
Due to the addition of a suction enhancer, it is a suspension that must be mixed diligently before each operation. It takes effect in 2 hours, reaches its peak in 6-10 hours, and the duration of action is 12-16 hours (depending on the dose). Usually, the higher the dose, the longer it lasts.
Long Action insulins are insulin analogues. Also transparent and colorless.
Long-acting insulins are: Levemir - Detemir (Novo Nordisk), Lantus (sanofi aventis)
Long-acting insulins
No need to shake before injection. It works up to 24 hours, so one, in some cases two injections are generally recommended. Has no pronounced peak, so the risk of developing hypoglycemia is very small between night and between meals.
In case of emergency, during operations, short-acting insulin during ketoacidosis is administered intravenously. It enters the bloodstream directly and begins to act.
Insulin therapy regimen
As already mentioned, a small amount of background insulin is produced continuously in the human body during the day - on average 0.5-1 one. Per hour. With glucose uptake, insulin secretion increases significantly with the amount of glucose taken.
During insulin therapy, the physiological mode of insulin secretion should be approached as closely as possible. Therefore, prolonged or long-acting insulin is necessary to create a daily background, and short-term or ultra-short-acting insulins during meals.
The insulin therapy regimen is chosen by the doctor for each patient individually, based on their characteristics.
There is insulin therapy 1. Traditional mode, During which short-term and prolonged insulins are taken simultaneously morning-evening, before breakfast and dinner. Such a regimen is less flexible, requires a strict schedule, and full compensation for diabetes is virtually impossible. Such a pattern is mainly found in adults with type 2 diabetes.
More convenient for children 2. Intensified insulin therapy., Which is more reminiscent of the action of a healthy pancreas.
Long-acting and prolonged-acting insulin is used as basal insulin. Long is done mostly once, twice in the morning-evening if necessary. In case of prolonged twice a day.
Finally, we use ultra-short, short-acting insulins before breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Extraordinary injections of ultra-short-acting insulin are also possible to correct glycemia.
Although the number of bites increases, intensified insulin therapy is more flexible, allowing quantitative changes in nutrition and food intake. The more we can adapt to individual needs, make changes on special days.
How to store insulin
Each insulin cartridge and vial, as well as all medications, has an expiration date.
To store insulin, it is necessary to store it in the refrigerator at a temperature of 2-8 degrees. Insulin should not be placed near the freezer as it loses activity during freezing.

Syringes-pens with insulin, which we use daily, can be stored at room temperature.
Insulin overheating is also not allowed. In summer we should not be exposed to direct sunlight.
We must have insulin in our handbag when traveling by plane. Do not carry insulin in your luggage.
When storage rules are not followed, insulin may leak and change color.
Insulin concentration
Today, insulin is mainly used all over the world, with a concentration of 100 units per ml.
In the past we found insulin with a concentration of 40 units per ml. Each cartridge is labeled with a concentration label.
Older, 40-unit syringes for insulin can still be found in pharmacies. Therefore, when using syringes, we must buy special 100-unit syringes so as not to confuse the doses.
Factors that affect the action of insulin:
While we may get identical doses of insulin over several days and the food may be exactly the same, it is quite possible to get different glycemic indexes.
There are many factors that affect the action of insulin, including:
Subcutaneous blood supply: increases with heating: eg sauna, jacuzzi, shower, bath, high temperature. Decreases: as a result of colds, tobacco consumption, dehydration.
Injection depth. It is absorbed faster from the muscle.
Injection site. It is absorbed most quickly from the abdomen, most slowly from the thigh.
Antibodies to insulin. Binds to insulin and lowers its action
Physical activity. Insulin is absorbed faster.
Massage the injection site. It is also absorbed faster.
Thickness of subcutaneous adipose tissue. The thicker it is, the slower it is absorbed
Injection in lipodystrophies.- Absorbed more slowly
What happens if a child refuses to eat?
In such a case, if the child is taking ultra-short-acting insulin, we do it after the meal, in reduced quantities, according to the food taken.
And if the child is on short-term insulin and we have already given the appropriate injection, then somehow we have to fill the acceptable bread units, we can offer more bread, which is usually less refused.
You may find yourself in a situation where you miss an insulin injection, what should we do?
It depends on which dose is missed:
1, dose before meals. If you remember soon, do the same dose as soon as you remember, or 1-2 units less, if 1-2 hours have elapsed, do half the dose, and if even more, add the next dose according to your glycemic index.
2, pre-sleep dose: If we are taking prolonged-acting insulin and remember it before 2pm, we are doing a 25-30% lower dose, or 1-2 units less, with each passing hour. If less than 5 hours remain before the morning injection, inject a half-dose of short-acting insulin, or 0.1 one / kg body weight.
If we take long-acting insulin, we do the usual dose in case of rapid recall, if we remember in the morning and we usually take insulin once a day, we do half the dose, or twice, we do the morning dose and we correct the glycemia with ultra-short insulin.






